Gold Testing with X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF)
Throughout history, gold has served as both a symbol of wealth and a form of money, and the need to ascertain its purity and authenticity has remained crucial. With the advent of testing technologies like X-ray fluorescence (XRF), testing for real gold has become expedient and easy.
XRF offers a non-destructive and highly efficient means of testing gold, allowing investors, jewelers, and collectors to buy solid gold with confidence.

X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) Principles and How it Works
X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the elemental composition of a material, including metals like gold. At its core, XRF relies on the fundamental principle of interaction between X-rays and atoms.
The process of XRF analysis involves three main steps: excitation, emission, and detection.
During excitation, the XRF instrument generates high-energy X-rays that bombard the sample. As a result, the sample's atoms release secondary X-rays, or fluorescent X-rays, which are unique to each element and serve as identifying signatures.
The emitted X-rays are then collected and sorted based on their energies using a detector. The XRF detector produces a spectrum that represents the distribution of detected X-ray energies, enabling the identification and quantification of the elements present in the sample.
The measured intensities of the emitted X-rays are proportional to the concentrations of the corresponding elements, allowing scientists and analysts to determine the material's composition accurately and non-destructively. Beyond precious metals testing, XRF is widely used in various industries, including mining, jewelry, archaeology, and environmental analysis, for its rapid and reliable elemental analysis capabilities.
Types of XRF Analyzers for Gold Testing
XRF analyzers generally fall into two main categories: handheld and benchtop. Handheld XRF analyzers are portable and compact devices that can be easily carried to the testing site. They are designed for quick and on-the-spot analyses, making them ideal for fieldwork, jewelry stores, precious metal dealerships, and on-site quality control.
Handheld analyzers offer the advantage of convenience and mobility, enabling users to analyze samples directly without the need for extensive sample preparation.

On the other hand, benchtop XRF analyzers are larger and more stationary instruments that are typically used in laboratory settings. These analyzers offer higher precision and sensitivity, making them suitable for in-depth and specialized analyses.
Benchtop analyzers may require more sample preparation and are generally used for research, complex material characterization, and strict quality control applications.
How XRF is Used to Test Gold
Using an XRF analyzer to test gold is remarkably easy and straightforward, making it an attractive option for professionals and non-experts alike.
The setup process is user-friendly, usually involving a few simple steps. As with some XRF analyzers used at The Safe House, these steps can be as simple as turning on the device and allowing it to calibrate to the operating environment in a few seconds. The X-ray testing machine is then ready to test the gold sample.
With a handheld XRF analyzer, the user positions the gold piece in front of the analyzer’s window or measurement area. For benchtop XRF analyzers, the gold piece is placed within the device’s compartment and closing the compartment.
Once the sample is in place, the operator initiates the analysis with a press of a button. The XRF analyzer then emits X-rays that excite the atoms in the gold piece, causing them to emit characteristic fluorescent X-rays.
The detector within the analyzer captures these emitted X-rays and processes the data in real-time. Within seconds, the results are displayed on the device's screen, providing information on the gold's purity and the concentrations of other elements.
Examples of X-ray Test Readings
Here are some sample X-ray test readings for different samples:
A. Pure Gold Testing
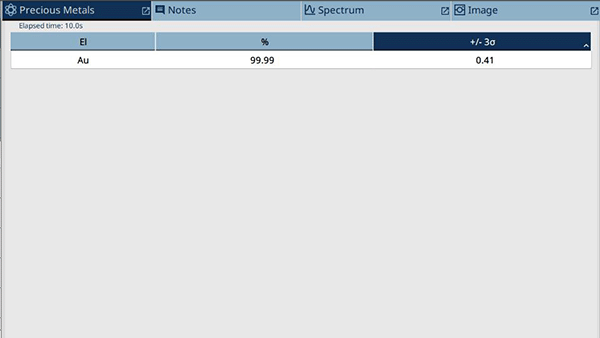
This gold testing result shows that the real gold piece is of 99.99% purity. 'Au' is the chemical symbol for gold. No other metals were detected on the sample's surface.
B. Pure Silver Testing
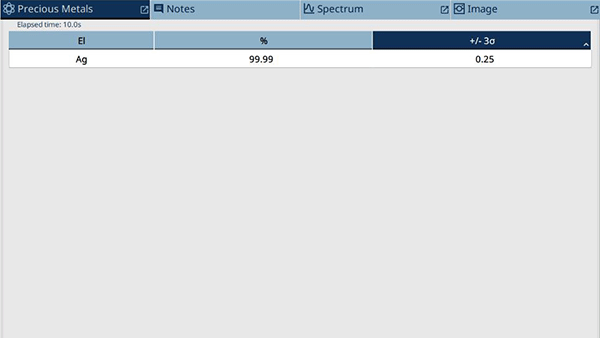
This silver testing result shows that the real silver piece is of 99.99% purity. 'Ag' is the chemical symbol for silver. No other metals were detected on the sample's surface.
C. Counterfeit Gold Testing
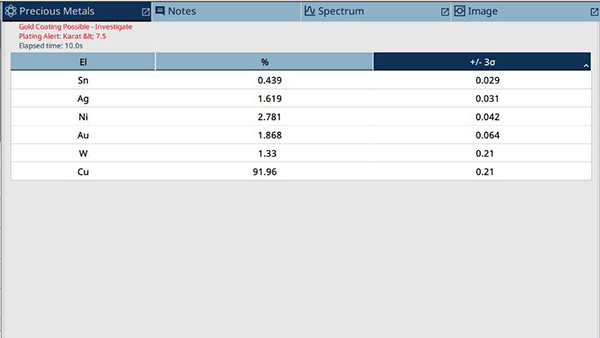
This test result can be representative of fake gold jewelry or fake gold bars where there is very little gold and higher percentages of other metals. In the image below, copper (Cu) is the main metal underneath the gold plating above.
D. Counterfeit Silver Testing
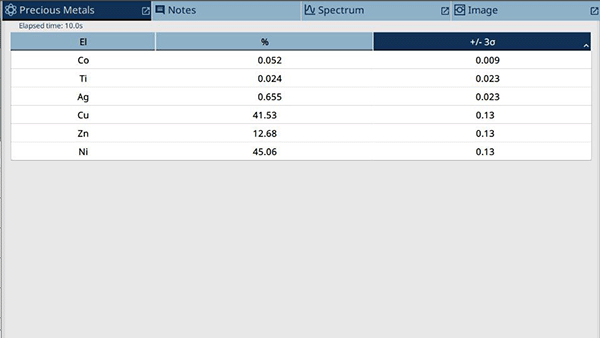
This test result shows that copper (Cu), nickel (Ni) and zinc (Zn) are the main metals in the fake silver piece sample.
Benefits of XRF fluorescence tests
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) tests offer a wide range of benefits, making them a popular and valuable analytical technique for gold testing:
- Non-Destructive Analysis: One of the most significant advantages of XRF tests is their non-destructive nature. The samples being analyzed remain intact throughout the process, making XRF ideal for analyzing precious metals, high-value artifacts, jewelry, and historical objects without causing any damage.
- Rapid Results: XRF tests provide almost instantaneous results. Within seconds, the instrument can determine the elemental composition of a material, enabling real-time decision-making and reducing analysis time significantly.
- Wide Element Range: XRF can detect and quantify a broad range of elements, from light elements like magnesium and aluminum to heavy elements like uranium and lead.
- Portable and Field-Deployable: Handheld XRF analyzers are portable and can be used in the field, allowing for on-site analysis without the need for sample transportation to a laboratory. This portability is particularly advantageous for field surveys, archaeological excavations, and in-the-field quality control.
Limitations of XRF fluorescence tests
While X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is a valuable and widely used technique for testing gold, it does have some limitations and disadvantages:
- Limited Penetration Depth: XRF has limited penetration depth, meaning it may not be suitable for analyzing very thick or large samples. For instance, if the gold item has thick gold plating or coating, the X-rays may not reach the core of the gold piece, leading to inaccurate results.
- Surface Sensitivity: XRF is primarily surface-sensitive, which means it analyzes only the outer layer of the sample. If the gold item has different compositions on different parts of the surface, the XRF analysis will be more representative if several points of the sample are tested.
- Calibration: Proper calibration and standardization are crucial for reliable XRF analysis. Calibrating the XRF instrument correctly with suitable reference samples is essential to achieve accurate and consistent results. Failure to calibrate adequately can lead to erroneous readings.
- Direct Contact: XRF relies on the physical interaction between the X-rays emitted by the analyzer and the surface of the sample. In situations where the sample's surface is irregular, rough, or covered with coatings or layers, obtaining accurate and representative results can be challenging. The X-rays may not effectively penetrate through thick coatings or reach the interior of the sample, leading to potentially misleading readings.
- Requires a Licensed Operator: Using an XRF analyzer often requires a licensed operator since the testing equipment emits radiation. In Singapore, only radiation workers with the R1 license can operate an XRF analyzer.
Despite these limitations, XRF remains a powerful and widely used technique for elemental analysis in various industries due to its non-destructive nature, rapid results, and versatility.
The Safe House Also Performs X-ray Fluorescence Tests
Since its inception in 2014, The Safe House has performed X-ray fluorescence tests for countless precious metals entering the vault’s premises. We conduct our non-destructive precious metals tests, including tests for density, thickness using ultrasound, surface composition using X-ray fluorescence, and electrical conductivity from our testing labs at The Reserve. Once completed, bullion tests can be accompanied by a precious metals testing report.
We have many years of experience testing gold and testing gold jewelry. Our gold testing machines are well able to detect different fake gold pieces and fake gold jewelry, from heavy gold plated bars, and gold filled with other metals, to gold alloys.
Please do not hesitate to contact us should you have any questions.
This article was originally published at: https://www.thesafehouse.sg/articles/gold-testing-with-x-ray-fluorescence-xrf
